Enhancing Healthcare Cybersecurity: The Role of CYLCOMED Pilots
The introduction of pilots in the CYLCOMED project marks a significant milestone in the effort to bolster cybersecurity in the healthcare sector. These pilots are not just testing grounds for new technologies; they are a strategic initiative to engage real end-users and gain critical insights into the challenges and opportunities of implementing innovative healthcare technologies.
This blog post explores the pivotal role of these pilots, the issues they address, and their potential impact on the healthcare industry.
A Shared Platform for Testing and Innovation
The CYLCOMED pilots are designed as shared platforms to explore several critical aspects:
- Cybersecurity: Ensuring that connected medical devices (CMDs) are secure from cyber threats.
- Overall Effectiveness: Evaluating the performance and utility of the technologies in real-world scenarios.
- Ethical Concerns: Addressing privacy, data protection, and ethical implications.
By focusing on these areas, the CYLCOMED pilots aim to facilitate the integration of new solutions into clinical practice, improve the work of clinicians, enhance the quality of patient care, and ensure the safety, security, and privacy of healthcare technologies.
The Increasing Connectivity and Vulnerabilities in Healthcare
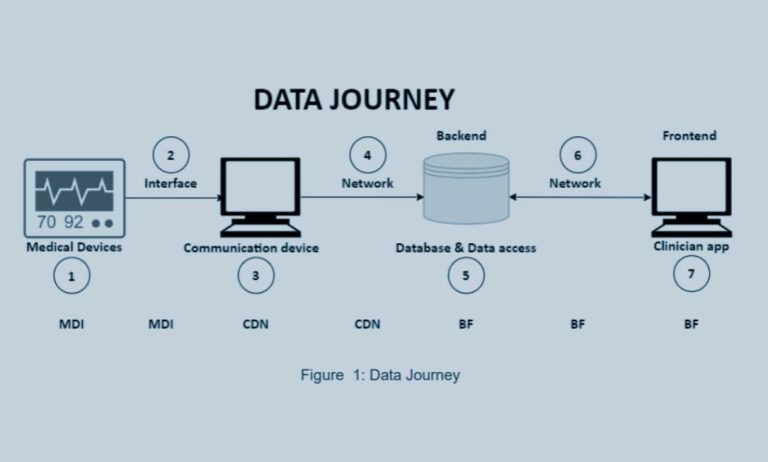
The healthcare sector is becoming increasingly interconnected, making it more vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Unlike the past, where patient records were stored in single, surveilled environments, modern digital healthcare involves numerous access points to sensitive information, which can be duplicated and distributed widely. This transformation has made healthcare organizations prime targets for cyber-attacks, with the potential to expose millions of patient records in a single breach.
Addressing Security and Privacy Challenges
Health technology solutions must adhere to stringent regulations and ethical standards. Recent studies have highlighted various privacy and policy issues, including:
- Security Threats: Cyber-attacks, vulnerabilities, and weaknesses in healthcare systems.
- Security Strategies: Techniques to detect, stop, or mitigate attacks.
The challenge for medical device manufacturers is to develop systems that are interoperable, secure, and scalable while ensuring effective risk management and data protection.
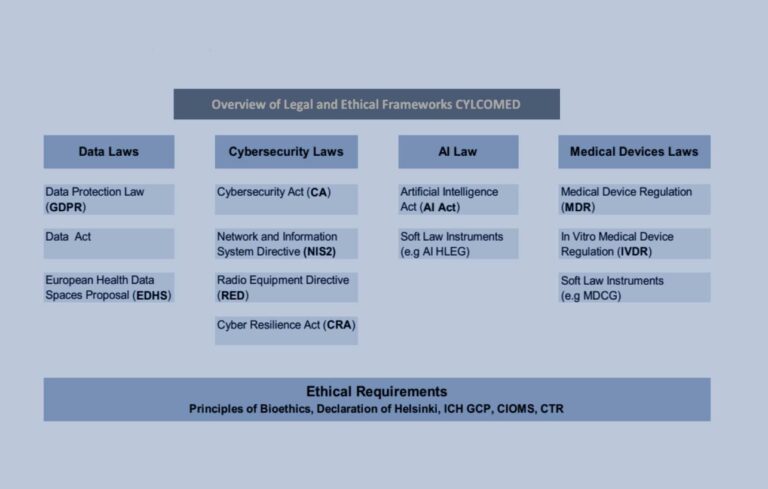
The Role of GDPR and Cyber-Hygiene
The implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe has been a significant step forward in harmonizing data privacy laws and addressing cybersecurity gaps. GDPR has increased the cost of breaches through fines and has heightened awareness around privacy and the need for improved cybersecurity measures.
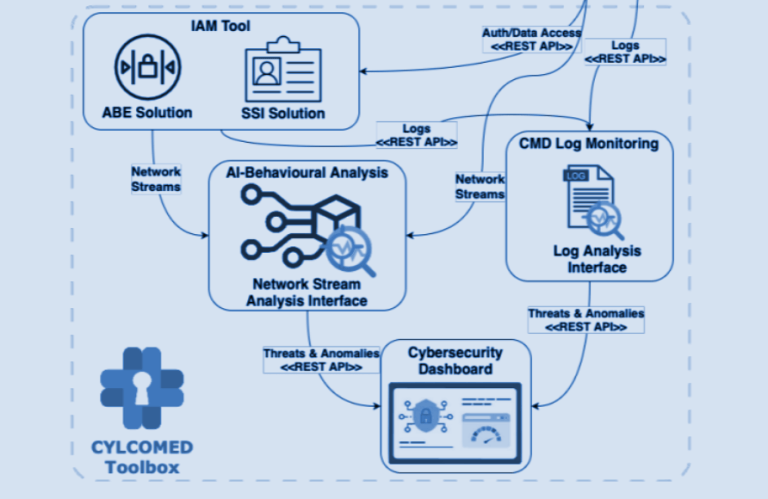
Healthcare organizations must integrate cybersecurity into their risk management processes. Essential practices include:
- Regular Backups: Ensuring resilience and quick recovery from attacks.
- Software Updates: Keeping systems up to date with security patches.
- Data Anonymization: Protecting patient identities by disassociating them from their medical data.
- Access Limitations: Restricting access to online patient information.
Security must be embedded in the design and lifecycle of all healthcare products, including electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine platforms, and connected medical devices.
The Collaborative Design and Diverse Stakeholder Involvement
The CYLCOMED project’s pilot design is driven by a user-centered approach, ensuring that the diverse needs of all stakeholders are met. This collaborative effort includes input from researchers, clinicians, policymakers, technical experts, and IT departments, ensuring a holistic assessment of the technologies.
The Neuromuscular Transmission (NMT) Intelligent Infusion Controller
A standout innovation within CYLCOMED Pilot 1 is the NMT intelligent infusion controller. This medical device monitors and regulates neuromuscular transmission vital signs, administering relaxant drugs to achieve specific target values. The controller represents a breakthrough in ICU automation and robotization, enhancing patient care through precise drug delivery.
RGB, the use case provider, is developing a family of controllers with innovative functionalities for integration into multiparameter monitors. The project aims to create a Hardware in Loop/Software in Loop (HiL/SiL) testbench platform to verify the system under laboratory conditions, addressing challenges such as:
- Compliance with Functional Requirements: Ensuring the system meets necessary standards.
- Physiological Behavior Testing: Simulating patient conditions to test performance.
- Security Compliance: Addressing non-functional requirements and overcoming CPU limitations.
The Impact and Future of CYLCOMED Pilots
The CYLCOMED pilots offer a comprehensive representation of the digital health sector, allowing for a thorough evaluation of the CYLCOMED toolbox from multiple perspectives. This ongoing process aims to provide valuable insights for developing a comprehensive prevention strategy, with detailed reporting in upcoming deliverables.
In conclusion, the CYLCOMED project and its pilots are paving the way for enhanced cybersecurity in healthcare, ensuring that new technologies can be safely and effectively integrated into clinical practice. By addressing cybersecurity, effectiveness, and ethical concerns, CYLCOMED is set to significantly impact the quality of patient care and the security of healthcare systems.