Advancing Cybersecurity in Connected Medical Devices
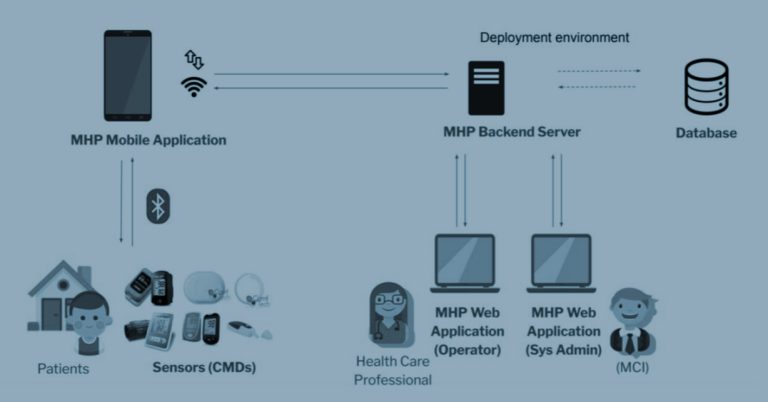
In the realm of healthcare, the security of medical devices is paramount. Cyber-attacks can disrupt any sector, but in healthcare, where cybersecurity lags behind, such disruptions can have life-threatening consequences. Medical device malfunctions pose significant risks to patients, and the theft of sensitive data can have long-lasting repercussions. Recognizing these challenges, the CYLCOMED project is dedicated to strengthening the cybersecurity of connected medical devices (CMDs), focusing on in vitro diagnostic tools and software as medical devices.
The Triple Perspective of CYLCOMED
The CYLCOMED project adopts a comprehensive approach to CMD cybersecurity, integrating three key perspectives:
- Medical Needs: Ensuring patient safety by maintaining the performance and safety of medical devices.
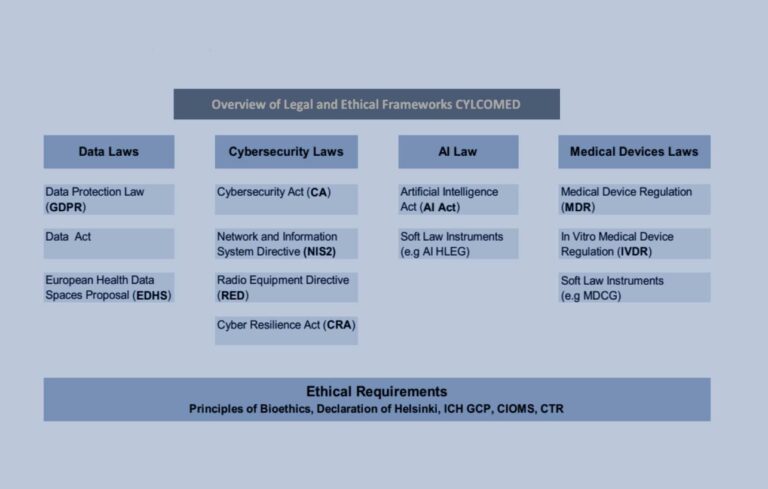
- Legal and Ethical Context: Addressing cybersecurity within the regulatory and ethical frameworks.
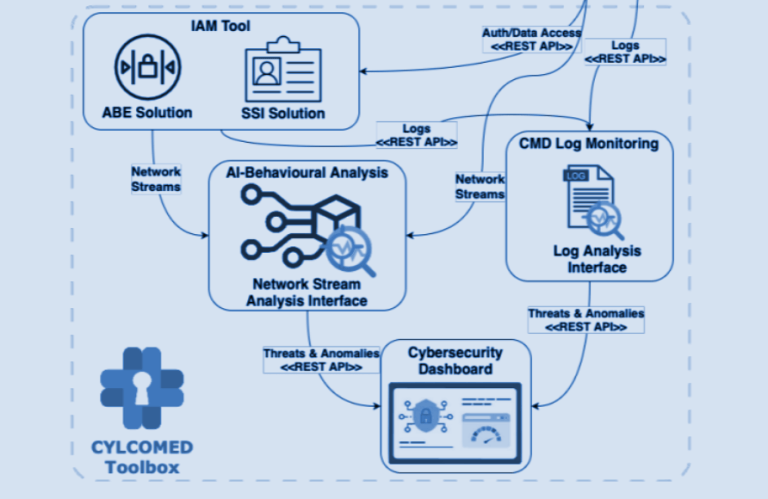
- Technical Expertise: Materializing cybersecurity requirements into practical software assets.
Key Insights
The foundation for CYLCOMED’s cybersecurity efforts identifies existing gaps and proposes new guidelines for stakeholders, offering a thorough analysis of applicable legal instruments and their intersections. Key points include:
- Cybersecurity Threats in Healthcare: The document highlights the critical nature of cybersecurity in healthcare, where device malfunctions can endanger lives, and data breaches can have long-term impacts.
- Existing Regulations and Standards: A comprehensive review of current regulations, standards, and best practices in medical device cybersecurity.
CYLCOMED’s Goals
- Maintain the performance and safety of medical devices.
- Ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of exchanged private data.
- Enable secure remote access to private data.
- Enhance cybersecurity awareness and training for healthcare staff, addressing the human factor in security.
Moving Forward
The identification of legal and regulatory challenges, particularly the need for potential revisions of MDCG 2019-16, is an ongoing effort. CYLCOMED aims to provide recommendations to regulators, policymakers, and lawmakers to advance the compliant use of innovative solutions for CMD cybersecurity. Based on the consortium’s experience, the project will make targeted recommendations to address the specificities of CMDs, IVDs, and SaMDs across different risk classes.
Conclusion
CYLCOMED project’s mission is to enhance the cybersecurity of connected medical devices. By integrating medical, legal, ethical, and technical perspectives, these documents provide a robust framework for developing secure and compliant CMD solutions. As the project progresses, these deliverables will continue to serve as foundational resources, guiding consortium partners and stakeholders toward a safer, more secure future in medical technology.